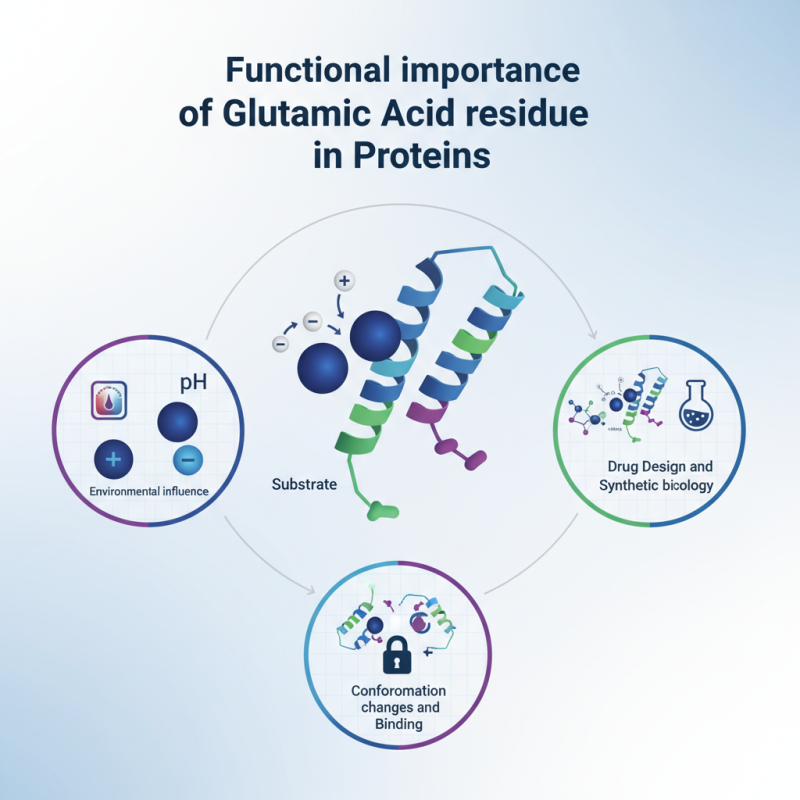
Why is Glutamic Acid Residue Important in Protein Function?
glutamic acid residue plays a crucial role in protein functionality. This amino acid, often found in enzymes and receptors, impacts various biological processes. For instance, its negative charge contributes to protein stability and interactions.
In enzymatic reactions, glutamic acid residue can act as a proton donor or acceptor. This capability enhances the enzyme’s catalytic efficiency. Moreover, its presence can influence the protein's conformational changes. These changes are essential for binding with substrates or other proteins.
However, not all glutamic acid residues function similarly. The surrounding environment affects their roles. Factors like pH and nearby amino acids can alter their behavior. Understanding these nuances is vital for drug design or synthetic biology. Reflecting on glutamic acid residue’s importance can lead to new discoveries in protein science.
Understanding Glutamic Acid Residue in Protein Structure
Glutamic acid, an amino acid, plays a crucial role in the structure and function of proteins. Its side chain contains a carboxylic acid group, giving it unique properties. This charge allows glutamic acid to participate in ionic interactions. Such interactions are vital for maintaining protein conformation. A stable structure is essential for the protein’s biological activity.
Research indicates that 25% of proteins in eukaryotes contain glutamic acid residues. These residues often serve as sites for post-translational modifications. For example, phosphorylation at glutamic acid can impact signal transduction. This relationship underscores the importance of glutamic acid in regulating cellular functions. However, variations in these residues can lead to dysfunctional proteins.
Interestingly, mutations in glutamic acid residues are linked to various diseases. For instance, alterations can disrupt enzyme activity. This disruption may lead to metabolic disorders. The intricate balance of glutamic acid is vital. It holds profound implications for understanding protein behavior in health and disease. Accessing related data might expose gaps in knowledge, highlighting areas for further research.
Importance of Glutamic Acid Residue in Protein Function
This chart illustrates the various roles that glutamic acid residue plays in protein function, showcasing its significant impact on enzyme activity, protein stability, signal transduction, neurotransmission, and metabolic regulation. Each percentage reflects the estimated contribution of glutamic acid in enhancing the protein's effectiveness in these functions.
Role of Glutamic Acid in Protein Folding and Stability
Glutamic acid plays a significant role in protein folding and stability. It is a polar amino acid, essential for maintaining the structure of proteins. Research from the Journal of Molecular Biology highlights that glutamic acid residues are critical in stabilizing protein conformations. These residues often form hydrogen bonds, contributing to the overall stability.
Additionally, a study in the Biophysical Journal reveals that proteins with a higher proportion of glutamic acid tend to fold more efficiently. This efficiency is crucial in cellular functions, where misfolded proteins can lead to diseases like Alzheimer’s. Glutamic acid's side chain can interact with other amino acids, creating a network that enhances stability.
However, not all interactions lead to positive outcomes. Sometimes, excessive glutamic acid can cause structural instability. Protein aggregation may occur, potentially leading to malfunction. Understanding this balance is vital for researchers working on protein engineering and therapeutics. The role of glutamic acid is complex, requiring careful consideration in both natural and engineered contexts.
Impact of Glutamic Acid on Enzyme Activity and Function
Glutamic acid, an amino acid, plays a crucial role in protein function. Its carboxyl group can donate protons, affecting protein structure. This property is vital for enzyme activity. Enzymes need precise shapes to function, influenced by the presence of glutamic acid.
For example, in certain enzymes, glutamic acid can act as a proton donor or acceptor. This action alters the enzyme's activity. This affects how substrates bind and how reactions proceed. Many enzymes rely on this residue for optimal function. Without it, the entire reaction can slow or stop.
Tips: Ensure you maintain proper pH for enzymatic reactions. Glutamic acid performs best in specific conditions. A small change can impact overall activity.
Consider the consequences when glutamic acid is missing. Enzyme activity may diminish, leading to broader metabolic issues. It's a reminder not to overlook small details in biochemical processes. Balancing these elements is crucial but often gets complicated. Each part must work together; failing to do so can lead to unexpected challenges.
Glutamic Acid Residue in Protein-Protein Interactions
Glutamic acid residues play a crucial role in protein-protein interactions. This amino acid, with its side chain carboxyl group, provides negative charges that facilitate binding between proteins. Recent studies suggest that approximately 35% of protein interactions involve aspartic and glutamic acid residues. Their negative charges attract positively charged residues in partner proteins, creating strong ionic bonds.
Tips: To enhance protein stability, consider the concentration of glutamic acid in your experiments. A higher concentration could improve interaction efficiency.
Moreover, glutamic acid can influence the shape and flexibility of proteins. Sometimes, these residues can disrupt interactions. For example, improper folding or mutations leading to excess glutamic acid can negate its positive effects. Research indicates that alterations in these residues may cause up to 15% of all protein misfolding diseases.
Tips: Monitor the pH during your studies. Since glutamic acid's behavior changes with pH, optimal conditions can greatly impact the study of protein interactions.
Clinical Importance of Glutamic Acid in Disease and Therapy
Glutamic acid, an amino acid, plays a crucial role in various biochemical processes. Its importance is particularly evident in the context of disease and therapy. This amino acid is a key player in neurotransmission, affecting mental health and neurological disorders. Alterations in glutamic acid levels can lead to conditions like Alzheimer's and schizophrenia.
In cancer research, glutamic acid is gaining attention. It influences tumor growth and metabolism. Therapies targeting glutamate pathways are being explored. This approach shows promise in slowing cancer progression.
Tip: Pay attention to your diet. Foods rich in glutamic acid like spinach and mushrooms can enhance overall health.
Understanding glutamic acid is essential. However, it's not without complexities. Researchers are still uncovering its multifaceted roles. This is a reminder of how much we still have to learn.
Tip: Regular check-ups can help monitor glutamic acid levels. This is crucial for early detection of potential health issues.

